前言:本文为学习 PyTorch深度学习快速入门教程(绝对通俗易懂!)【小土堆】时记录的 Jupyter 笔记,部分截图来自视频中的课件。
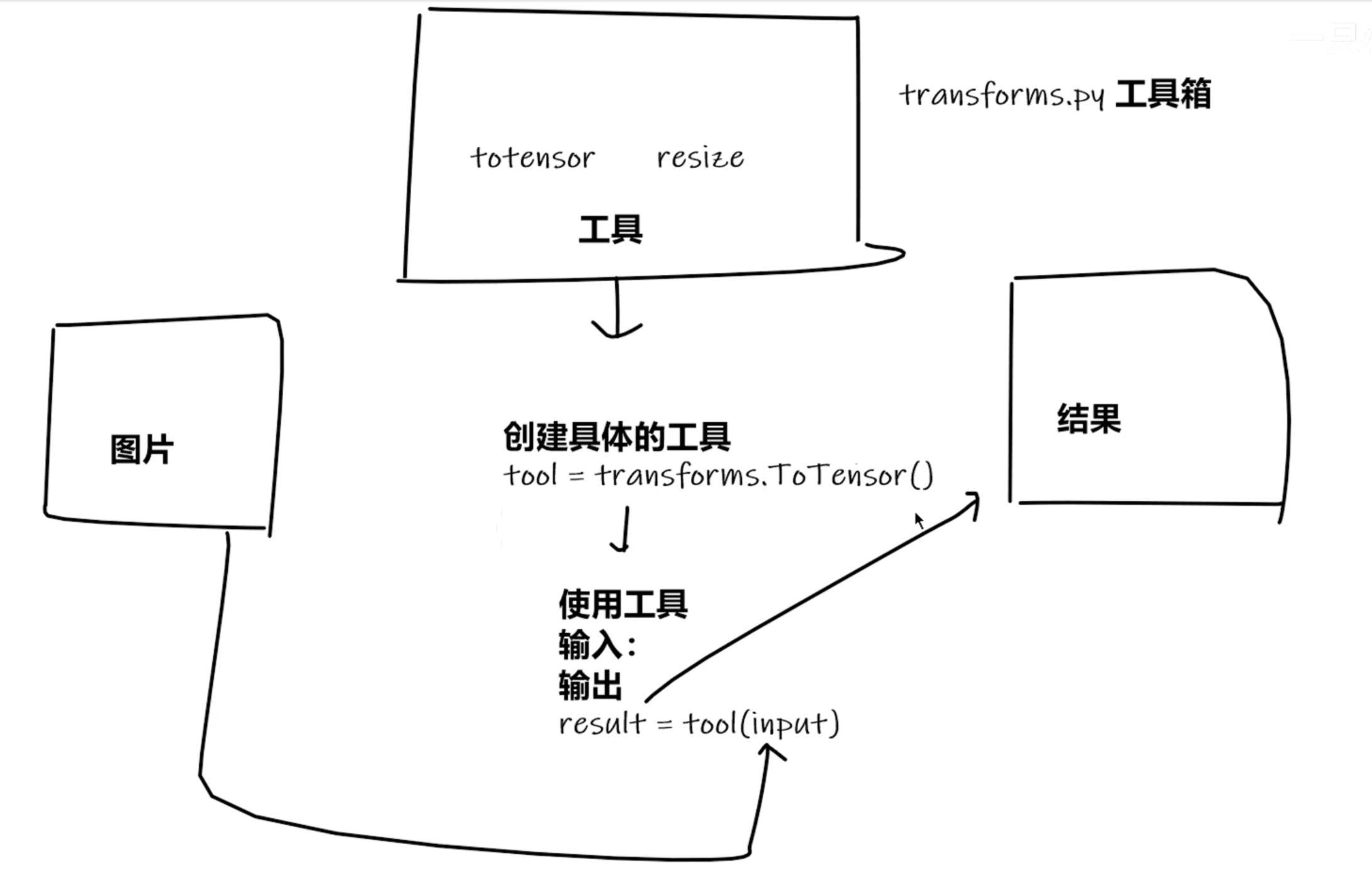
本文主要通过 transform.ToTensor 解决两个问题:
- transform如何使用
- tensor数据类型的特色
from torchvision import transforms
from PIL import Image
img_path = "D:/work/StudyCode/jupyter/dataset_for_pytorch_dataloading/train/ants/0013035.jpg"
img = Image.open(img_path)
print(img)
<PIL.JpegImagePlugin.JpegImageFile image mode=RGB size=768x512 at 0x1FE4AA30940>
tensor_trans = transforms.ToTensor()
tensor_img = tensor_trans(img)
tensor_img.shape
torch.Size([3, 512, 768])

可以看到Tensor数据类型中有很多属性,除了data即数据属性外,还有一些比较重要的属性:
backward_hooks用于反向传播_grad记录梯度device记录数据存储在什么设备上(GPU or CPU)dtype记录数据类型requires_grad表示是否跟踪梯度
可以看到这些属性都是与神经网络关系密切的,所以tensor在纯数据的基础上,可以看成是一个针对神经网络所需参数打包后的一个数据类型。
import cv2
cv_img = cv2.imread(img_path)
type(cv_img)
numpy.ndarray
使用OpenCV读取图片可以发现是ndarray类型的数据,而ToTensor方法支持ndarray类型和PIL类型,刚好对应了两种主要的图片读取方法。
下面介绍一个Python对象中的内置的实例方法:
call方法:
可以看到 内置方法 __call__ 本质就是在类中重载 () 运算符,使得类实例对象可以像调用普通函数那样执行 __call__ 中的函数
# call的用法
class Person:
def __call__(self, name):
print("__call__ "+"Hello "+name)
def hello(self, name):
print("hello " + name)
person = Person()
person("Here_SDUT")
person.hello("lisi")
__call__ Hello Here_SDUT
hello lisi
Compos方法
用于将多种transform方法打包起来,具体用法可以看Example
class Compose(builtins.object)
| Compose(transforms)
|
| Composes several transforms together. This transform does not support torchscript.
| Please, see the note below.
|
| Args:
| transforms (list of ``Transform`` objects): list of transforms to compose.
|
| Example:
| >>> transforms.Compose([
| >>> transforms.CenterCrop(10),
| >>> transforms.PILToTensor(),
| >>> transforms.ConvertImageDtype(torch.float),
| >>> ])
ToTensor方法
用于将PIL类型或者ndarray类型的数据转换成Tensor类型,具体可以见前文
Normalize方法
输入为 Tensor 数据类型,进行归一化,缩小数据的范围
class Normalize(torch.nn.modules.module.Module)
| Normalize(mean, std, inplace=False)
|
| Normalize a tensor image with mean and standard deviation.
| This transform does not support PIL Image.
| Given mean: ``(mean[1],...,mean[n])`` and std: ``(std[1],..,std[n])`` for ``n``
| channels, this transform will normalize each channel of the input
| ``torch.*Tensor`` i.e.,
| ``output[channel] = (input[channel] - mean[channel]) / std[channel]``
|
| .. note::
| This transform acts out of place, i.e., it does not mutate the input tensor.
|
| Args:
| mean (sequence): Sequence of means for each channel.
| std (sequence): Sequence of standard deviations for each channel.
| inplace(bool,optional): Bool to make this operation in-place.
trans_norm = transforms.Normalize([0.5,0.5,0.5],[0.5,0.5,0.5]) # 一般写法,可以使得数据缩小的到[-1,1]的范围内
img_norm = trans_norm(tensor_img)
img_norm[0][0][0] # 查看数据,发现处于 [-1,1]内
## 这里也可以将图片放入tensorboard进行可视化查看
tensor(-0.3725)
Resize方法
class Resize(torch.nn.modules.module.Module)
| Resize(size, interpolation=<InterpolationMode.BILINEAR: 'bilinear'>, max_size=None, antialias=None)
|
| Resize the input image to the given size.
| If the image is torch Tensor, it is expected
| to have [..., H, W] shape, where ... means an arbitrary number of leading dimensions
|
| Args:
| size (sequence or int): Desired output size. If size is a sequence like
| (h, w), output size will be matched to this. If size is an int,
| smaller edge of the image will be matched to this number.
| i.e, if height > width, then image will be rescaled to
| (size * height / width, size).
type(img)
img.size
trans_resize = transforms.Resize((512,512))
img_resize = trans_resize(img)
img_resize.size
type(img_resize)
PIL.JpegImagePlugin.JpegImageFile
(768, 512)
(512, 512)
PIL.Image.Image
# 使用Compose对象 将图片压缩后转为tensor类型
trans_resize_2 = transforms.Resize((512,512))
trans_compos = transforms.Compose([trans_resize_2, transforms.ToTensor()])
img_resize_2 = trans_compos(img)
img_resize_2.shape
type(img_resize_2)
torch.Size([3, 512, 512])
torch.Tensor
RandomCrop的用法
随机裁剪操作
class RandomCrop(torch.nn.modules.module.Module)
| RandomCrop(size, padding=None, pad_if_needed=False, fill=0, padding_mode='constant')
|
| Crop the given image at a random location.
| If the image is torch Tensor, it is expected
| to have [..., H, W] shape, where ... means an arbitrary number of leading dimensions,
| but if non-constant padding is used, the input is expected to have at most 2 leading dimensions
|
| Args:
| size (sequence or int): Desired output size of the crop. If size is an
| int instead of sequence like (h, w), a square crop (size, size) is
| made. If provided a sequence of length 1, it will be interpreted as (size[0], size[0]).
| padding (int or sequence, optional): Optional padding on each border
| of the image. Default is None. If a single int is provided this
| is used to pad all borders. If sequence of length 2 is provided this is the padding
| on left/right and top/bottom respectively. If a sequence of length 4 is provided
| this is the padding for the left, top, right and bottom borders respectively.
|
trans_random = transforms.RandomCrop((200,300))
# trans_compos_2 = transforms.Compose([trans_random, transforms.ToTensor()])
img_random = trans_random(img)
img_random

对于其他transform中的工具,可以按照以下步骤自行探索:
- 使用help命令查看用法或者翻阅官方文档
- 看函数的输入和输出是什么
- 关注方法需要什么参数以及参数的意义
- 不知道返回值的时候:
- print一下
- print(type())
- debug
- 最后查阅网上资料

